Delicata squash Nutrition facts
Delicata squash is a pleasantly sweet, orange-fleshed winter squash in the Cucurbita family of vegetables. It is distinguished from other winter squash members in having a long cylindrical shape and delicate cream/copper skin with dark forest-green vertical stripes. Skin is thin and edible, unlike in other winter squash varieties.
Botanical name: Cucurbita pepo.
Delicata squash is also known as the peanut squash, sweet-potato squash, etc.
 |
| Delicata squash. Courtesy: Dyogi |
Delicata squash belongs to the family of winter squashes and can be harvested when fully mature and stored for several months—unlike summer squashes such as zucchini, which have a short shelf life.
Delicata seeds require a warm soil temperature of around 70°F (21°C) for proper germination. Seedlings are typically planted in early spring, once the frost risk has passed. This variety thrives in well-drained soil enriched with organic matter for healthy growth.
Like other winter squash varieties, Delicata squash is monoecious, meaning it produces separate male and female flowers on the same plant. The fruits begin to form about 70 days after planting and are ready for harvest in 90–100 days.
It is cylindrical with a grooved skin, rounded ends, and cream or yellow color accented by green stripes along its length. Its thin skin is edible and tender when cooked.
Harvesting is ideally done when the leaves begin to dry and the stem turns brown and hard. The fruits are then sun-cured for 1–2 weeks before storing them in a cool, dry place. Each fruit measures about 4–6 inches long and 2–3 inches wide, weighing approximately 1–1.5 pounds.
Inside, the Delicata squash flesh is orange-yellow with a central hollow cavity filled with large, flat seeds—similar to those of a pumpkin. The flesh has a firm texture, a sweet flavor, and a rich yellow color when cooked.
Popular Delicata Varieties:
Sweet Dumpling – A slightly flattened variety with tender, flavorful flesh.
Sugar Loaf – Very sweet and oval-shaped, known for its excellent flavor.
Honey Boat – A boat-shaped variety featuring a very sweet, rich taste.
See the differences between Summer and Winter variety squashes in an infographic:
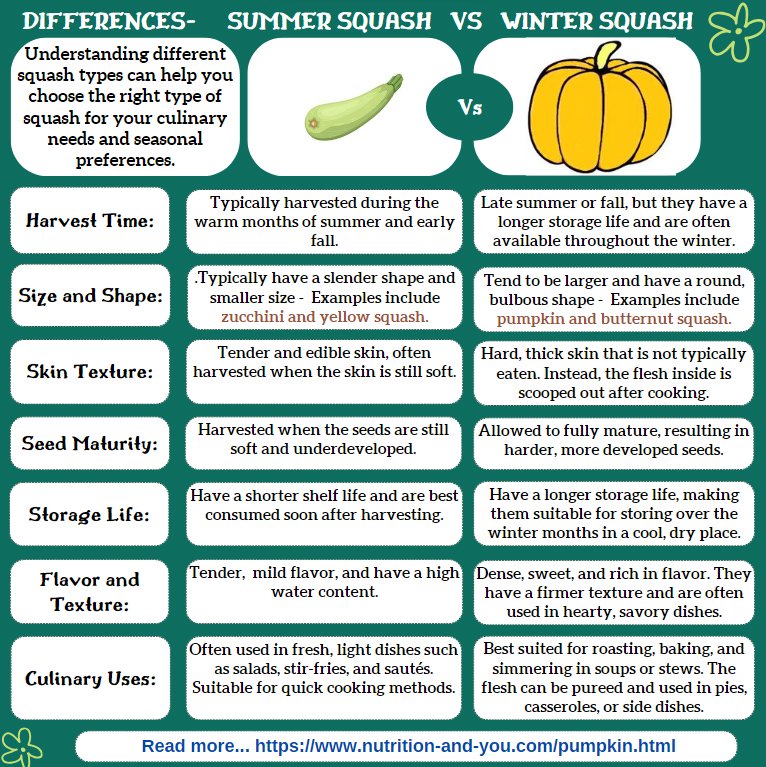 |
Health Benefits of Delicata Squash
Delicata squash is a low-calorie winter squash—a 3.5 oz (100 g) serving provides just 34 calories, similar to acorn squash (40 cal/100 g). It’s an excellent choice for those aiming for weight management and healthy eating.
This squash contains no saturated fats or cholesterol. Its thin, edible peel is a valuable source of both soluble and insoluble dietary fiber, which supports digestive health and helps maintain a healthy gut.
Delicata squash is a naturally gluten-free food, making it a perfect option for individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease.
It is a rich source of carotenoids and vitamin A, providing approximately 1370 IU of vitamin A and 820 µg of ß-carotene per 100 g. Vitamin A acts as a powerful antioxidant that supports cell growth, mucosal repair, healthy vision, and cancer prevention.
Together with vitamin A, its pigment compounds help eliminate harmful free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) from the body—reducing oxidative stress and slowing down the aging process.
Fresh Delicata squash also provides higher levels of vitamin C (20% of RDA per 100 g), pyridoxine (vitamin B6), and thiamin compared to pumpkin. Vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis in bones, cartilage, and blood vessels, and also aids in iron absorption.
It supplies about 24 µg (6% RDA) of folates per 3.5 oz serving. Folate is vital for cell division and DNA synthesis. Adequate folate intake during early pregnancy helps prevent neural tube defects in newborns.
Like other winter squash varieties, Delicata squash is low in sodium (3 mg/100 g) but high in potassium (350 mg/100 g)—an essential heart-friendly electrolyte that helps lower blood pressure and regulate heart rate by balancing sodium levels.
Additionally, Delicata squash offers modest amounts of B-complex vitamins such as thiamin, pantothenic acid, and riboflavin, along with key minerals including selenium, calcium, iron, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc, all contributing to metabolic health and immune function.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percent of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 34 Kcal | 1.7% |
| Carbohydrates | 8.59 g | 6.6% |
| Protein | 0.95 g | 1.7% |
| Total Fat | 0.13 g | <1% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 1.5 g | 4% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 24 μg | 6% |
| Niacin | 0.500 mg | 3% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.188 mg | 4% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.156 mg | 12% |
| Riboflavin | 0.062 mg | 5% |
| Thiamin | 0.030 mg | 2.5% |
| Vitamin-A | 1370 IU | 45.5% |
| Vitamin-C | 12.3 mg | 20.5% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 4 mg | <0.5% |
| Potassium | 350 mg | 7% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 28 mg | 3% |
| Iron | 0.58 mg | 7% |
| Magnesium | 14 mg | 3.5% |
| Manganese | 0.163 mg | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 23 mg | 3% |
| Selenium | 0.4 µg | <1% |
| Zinc | 0.21 mg | 2% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 820 μg | -- |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 0 μg | -- |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 38 μg | -- |
Selection and Storage
Winter squash (also called hard squash) is typically grown during the warm season and can be stored for several months, lasting well through the winter season.
Delicata squash is in peak season from October to January and commonly available in farmers' markets. Choose fresh, medium-sized fruits with dry, firm, and intact stems. Avoid squash with a broken stem, surface blemishes, or any cuts and punctures, as these may indicate spoilage.
At home, whole Delicata squash can be stored for about 2–4 months or even longer when kept in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated place.
Cut sections of Delicata squash should be used immediately in cooking for the best flavor and texture. For short-term storage (up to 1–2 days), wrap the pieces in plastic wrap and keep them in the refrigerator at high humidity settings.
Preparation and Serving Methods
Delicata squash is a popular winter vegetable in the United States and Canada, known for its sweet flavor and tender texture. It is ideal for a variety of cooking methods including baking, roasting, steaming, boiling, and sautéing.
Unlike many other hard-skin winter squashes, the thin skin of Delicata squash is easy to cut and remains edible after cooking, eliminating the need for peeling.
The squash maintains its shape well during cooking, making it perfect for stuffed squash recipes and baked dishes.
You can also slice it into rings or cubes and add it to various dishes such as soups, salads, stews, gratins, sandwiches, or risotto—adding both flavor and nutrition.
 |
| Suffed delicata squash. |
Here are some serving tips:
Cut Delicata squash in half, scoop out the seeds, and stuff it with a mix of quinoa, meat, cheese, mushrooms, leafy greens (spinach), and fresh herbs. Then bake it in the oven for a warm, nutrient-rich meal.
Prepare a comforting Delicata squash gratin combined with seasonal vegetables or sausage for a hearty dish full of flavor.
Mashed or pureed Delicata is a nutritious, low-calorie alternative to traditional mashed potatoes, offering a naturally sweet and creamy taste.
Delicata squash soup makes a rich, creamy, and comforting meal, perfect for cooler months.
Delicata squash seeds can be enjoyed as a healthy snack—simply toast the kernels in the oven for a crunchy, protein-rich treat.
Safety Profile
Allergic reactions to Delicata squash are rare. It is considered safe for pregnant women and infants when consumed as part of a balanced diet. (Medical disclaimer)
Read further on:
≻≻- Spaghetti squash nutrition facts.
≻≻- Butternut squash nutrition facts.
≻≻- Buttercup squash nutrition facts.
≻≻- Pattypan squash nutrition facts.
≻≻- Kabocha squash nutrition facts.
≻≻- Back to Vegetables from Delicata Squash nutrition. Visit here for an impressive list of vegetables with complete illustrations of their nutrition facts and health benefits.
≻≻-Back to Home page.
Further reading:
Garden Mastery Tips- WSU Clark County Extension.
Watch your garden grow- University of Illinois Extension (PDF).