Butternut squash nutrition facts
Butternut squash is one of the most popular winter squash vegetables. Butternuts grow on an annual, long trailing vine. This variety of squash is widely cultivated under warmer climates of South and Central America for its edible fruits, blossoms (flowers), as well as seeds.
Botanically, it belongs to the Cucurbitaceae family of field pumpkins; probably originated in the Central American region. In the markets, they are often identified as giant pear-shaped, golden-yellow pumpkins instead of squash.
Scientific name: Cucurbita morschata.
 |
| Butternut squash in a market. Courtesy: Indiamart |
Butternut, in fact, is the most common winter squash vegetable. It is monoecious (separate male and female flowers appear on the same plant) as in pumpkins. Honeybees help in pollination and productive fruiting.
Butternut is a big-sized fruit featuring an elongated, thick neck that is attached to a pear-shaped, broad lower base. Its external surface has smooth ribbed skin. Even so, the butternut varies widely in its shape and size with individual fruit weighing up to 15 kilos.
On its interior, its flesh is golden-yellow to orange depending on the extent of carotene pigments in its flesh. A cross-section at the lower bulge reveals a central hollow cavity filled with a mesh-like network of mucilaginous fibers interspersed with flat elliptical seeds. The seeds are similar to that of Pepita (pumpkin seeds).
 |
| Young butternut squash in a garden! Courtesy:jspatchwork |
Butternut squash seeds are nutritious and contain 35-40% oil, and 30% protein. In Argentina, the whole crop is also grown to feed livestock.
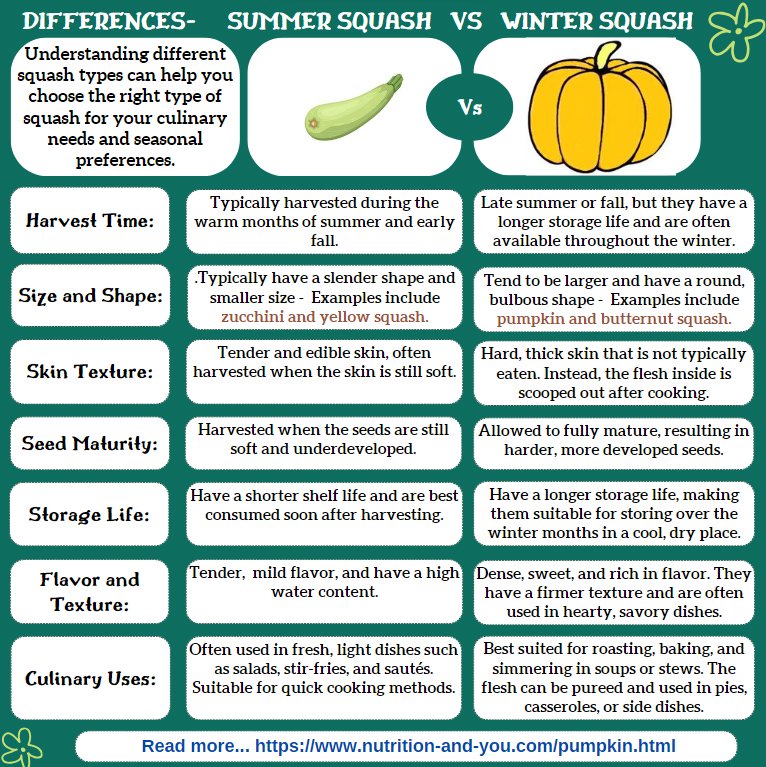
See the differences between Summer and Winter variety squashes in an infographic:
 |
Health benefits of Butternut squash
Butternut squash is composed of many vital polyphenolic antioxidants and vitamins. Like in other Cucurbitaceae members, butternut also has very low calories, 100 g provides just 45 calories. It contains no saturated fats or cholesterol. Nonetheless, it is a rich source of dietary fiber and phytonutrients. Squashes are the most often recommended vegetables by dieticians in cholesterol-controlling and weight-reduction programs.
Butternuts have more vitamin-A than that of in pumpkins. At 10,630 IU per 100 g, it, perhaps, is the single vegetable source in the Cucurbitaceae family with the highest levels of vitamin A, constituting about 354% of RDA. Vitamin A is a powerful natural anti-oxidant and is required by the body for maintaining the integrity of skin and mucosa.
Vitamin A is also an essential element for healthy eyesight. Research studies suggest that natural foods rich in vitamin A help the human body protect against lung and oral cavity cancers.
Furthermore, butternut squash composes plenty of natural polyphenolic flavonoid compounds like a and ß-carotenes, cryptoxanthin-ß, and lutein. These pigment chemicals convert into vitamin A inside the body and carry out the same protective functions as this vitamin.
It is rich in the B-complex group of vitamins like folates, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B-6 (pyridoxine), thiamin, and pantothenic acid.
It has a similar mineral profile as that of pumpkin; containing adequate levels of minerals like iron, zinc, copper, calcium, potassium, and phosphorus.
Butternut squash seeds are an excellent source of dietary fiber and mono-unsaturated fatty acids that benefit heart health. Also, they are rich in protein, minerals, and numerous health-benefiting vitamins.
The seeds are excellent sources of health-promoting amino acid, tryptophan. Tryptophan converts to health-benefiting GABA neurochemicals in the human brain.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percent of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 45 Kcal | 2% |
| Carbohydrates | 11.69 g | 9% |
| Protein | 1.0 g | 2% |
| Total Fat | 0.1 g | 0.5% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 2 g | 5% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 27 µg | 7% |
| Niacin | 1.200 mg | 8% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.400 mg | 8% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.154 mg | 12% |
| Riboflavin | 0.020 mg | 2% |
| Thiamin | 0.100 mg | 8% |
| Vitamin A | 10630 IU | 354% |
| Vitamin C | 21 mg | 35% |
| Vitamin E | 1.44 mg | 10% |
| Vitamin K | 1.1 µg | 1% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 4 mg | 0.5% |
| Potassium | 352 mg | 7% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 48 mg | 5% |
| Copper | 0.072 mg | 8% |
| Iron | 0.70 mg | 9% |
| Magnesium | 34 mg | 9% |
| Manganese | 0.202 mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 33 mg | 5% |
| Selenium | 0.5 µg | <1% |
| Zinc | 0.15 mg | 1% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-α | 834 µg | -- |
| Carotene-ß | 4226 µg | -- |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 3471 µg | -- |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 0 µg | -- |
Selection and storage
Butternut squash, being a member of the winter squash vegetables, can be readily available in the USA markets from September until the middle of December. However, since they are imported from the South American countries to the US they can be easily procured year-round.
Buy fresh whole butternut squash instead of its cut sections. Look for mature produce that features a fine woody note on tapping, and is heavy in hand. Its stem should be stout and firmly attached to the fruit.
Avoid those with wrinkled surfaces, spots, cuts, and bruises.
Once at home, mature squash can be stored for many weeks in a cool, humid-free, well-ventilated place at room temperature. However, cut sections should be placed in the refrigerator and wrapped in a plastic bag where they keep well for a few days.
Preparation and serving methods
As in pumpkins, some hybrid squash varieties are subjected to insecticide powder or spray. Therefore, wash them thoroughly under running water to remove dirt, soil, and any residual insecticides/fungicides.
Long-neck butternut fruit contains more meat, shallow cavities, and fewer seeds. Trim the stem end and slice the whole fruit into two halves. Remove the inner net-like structure and set aside the seeds. In general, wedges/small cubes can be employed in the recipes.
Butternut's unique golden-yellow color is due to yellow-orange phenolic pigments in their skin and flesh.
Almost all the parts of the butternut squash plant; fruit, leaves, flowers, and seeds are edible.
Here are some serving tips:
 |
| Butternut quash wedges and soup. Courtesy: sinksanctity and Courtesy: karenandbrademerson |
Being a member of the pumpkin family, butternut squash has a pleasant musky flavor and mildly sweet taste. Fresh, raw butternut cubes may add a special crunchiness to vegetable salads.
It is a favorite of chefs in both savory as well as sweet dishes. It can be used in a variety of delicious recipes as baked, stuffed, or stir-fried. Steam cook to get maximum nutrients.
In Mexico, butternut squash bisque (soup) with added fruits, herbs, or seafood is a favorite appetizer.
As in pumpkins, it can also be used in the preparations of casseroles, pies, pancakes, custard, ravioli, bread, and muffins.
Roasted and tossed butternut squash seeds can be used as snacks.
As in pumpkins and zucchini, squash flowers too can be stuffed with cheese or added to soups.
Safety profile
Butternut squash has no known reported cases of allergic reactions. Pregnant and nursing mothers can eat it safely. However, being a member of cucurbits, some fruits may carry cucurbitacin toxin. Therefore, bitter-tasting butternuts, raw or cooked, should be completely avoided. (Medical disclaimer).
You may also like to read≻≻-
≻≻-Kabocha squash nutrition facts and health benefits.
≻≻-Buttercup squash nutrition facts and health benefits.
≻≻-Acorn squash nutrition facts and health benefits.
≻≻-Crookneck squash nutrition facts and health benefits.
≻≻-Back to Vegetables from Butternut Squash nutrition. Visit here for an impressive list of vegetables with complete illustrations of their nutrition facts and health benefits.
≻≻-Back to Home page.
Further reading and Resources:
Stanford School of Medicine Cancer information Page- Nutrition to Reduce Cancer Risk. (Link opens in new window).