Black Gram (उड़द) Nutrition facts
Black gram, also known as vigna mungo beans, are diminutive, black, dried beans that hold a significant place in Asian culinary traditions. These small legumes belong to the Fabaceae or Leguminosae family, specifically within the genus Vigna.
Scientific name: Vigna mungo L.
 |
| Black gram (urad) beeans, whole and hulled. |
The beans, commonly referred to as urad, are the pods of a plant originating from India. This plant is an annual, drought-tolerant, dicotyledonous legume that thrives in sandy, loamy soil. After 60-70 days from seedling, small, hairy, cylindrical pods measuring 4-7 cm in length develop. Each pod contains 6-10 seeds that come in black, grayish, brown, or dark green colors, with a creamy white interior.
Black gram (Vigna mungo) is divided into two subspecies:
V. mungo var. niger: This category comprises varieties that exhibit early maturity and produce dark, black seeds.
V. mungo var. viridis: This category consists of varieties that mature later, with small, green seeds.
Health Benefits of Black Gram
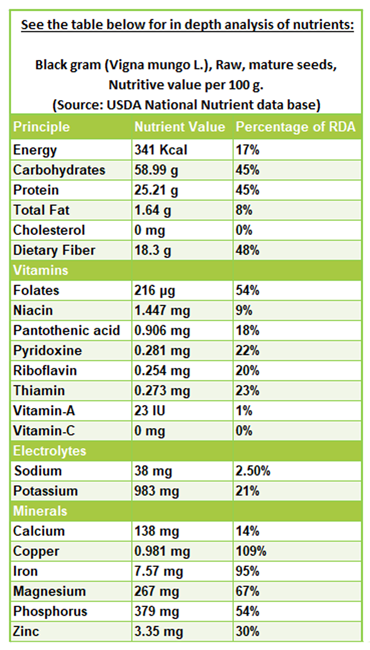
Black gram beans contain 341 calories and offer 25.21 g or 45% of the recommended daily value of protein. Despite their lower calorie count, these beans boast a higher protein content compared to chickpeas.
Black gram beans stand out among legumes due to their soluble mucilaginous polysaccharides, providing excellent levels of dietary fiber. This fiber acts as a bulk laxative, safeguarding the colon mucosa by reducing exposure to toxins and binding to potential cancer-causing substances in the colon. Moreover, dietary fiber has been demonstrated to lower blood cholesterol levels by reducing the reabsorption of cholesterol-binding bile acids in the colon.
Urad beans contain small amounts of isoflavones, including glycitein, genistein, daidzein, and formononetin. These isoflavones have been associated with reducing the risk of post-menopausal cancers and osteoporosis.
These beans are rich sources of B-complex vitamins, particularly folates, providing 216 μg or 54% of daily values per 100 g. Folate, along with vitamin B-12, is crucial for DNA synthesis and cell division, potentially preventing neural tube defects in newborns when consumed adequately around conception and during pregnancy.
Additionally, urad beans contain significant levels of various B-complex vitamins, including vitamin B6 (22%), thiamin (23%), pantothenic acid (18%), riboflavin (20%), and niacin (9%) of daily recommended values. These vitamins act as co-factors for enzymes involved in carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism.
Urad beans are also excellent sources of minerals, with high levels of iron providing 7.57 mg or 95% of the recommended daily intake (RDI). Iron supports memory, cognition, and helps prevent anemia. Additionally, these beans contain abundant amounts of calcium (14%), copper (109%), magnesium (67%), zinc (30%), and phosphorus (54%) of the daily values.
Furthermore, they are rich in potassium, offering 983 mg (21%) per 100 g, nearly 1.5 times more than in chickpeas. Potassium, an electrolyte present in cell and body fluids, helps counteract the adverse effects of sodium on heart and blood pressure.
Selection and Storage
Harvesting occurs once the entire plant and seed pods have turned yellow. The harvested crops are then dried under the sun. Typically, threshing and winnowing methods are utilized to separate the seeds.
Black gram beans are readily available in stores throughout the year. Look for well-formed, bold-black dry seeds sold in bins and packets. Alternatively, shops may offer ready-to-use split, hulled, and cleaned beans.
At home, store dry beans in an air-sealed plastic or metallic container, keeping them in a cool, dry place away from high temperatures and humidity.
At home, store dry beans in an air-sealed plastic/metallic bin and keep them in a cool, dry place away from high temperatures and humidity.
Preparation and Serving ideas
Clean urad beans should be soaked for 6-10 hours prior to cooking for optimal results. This soaking method, followed by pressure cooking, is a time-efficient approach.
Dried, mature urad seeds, boasting a delicate texture and robust flavor, are cooked using methods similar to those employed for other legumes.
Here are some serving tips:
 |
| South-Indian style-Dosa sambar. |
In India, urad lentils are processed by hulling and splitting, often combined with rice to create dishes like dosa (தோசை) or the spiced lentil puree dal makhani (दाल मखनी).
South Indian cuisine utilizes a mixed batter of rice and urad for making idli and urad vada (medu vada), typically served with coconut chutney and sambar (vegetable stew).
Urad can also be ground into flour for various purposes such as confectionery, flatbreads, or regular bread.
In Sri Lanka and Kerala, similar batter is used in Uttappam, a dish served with vegetables, fish, or chicken curry.
Hulled urad split lentils are commonly used in the preparation of papadum (papad- पापड़) across many Indian regions.
Whole urad beans can be sprouted and added to salads for a nutritious twist.
Safety Profile
When consumed in small amounts, black mungo typically doesn't cause flatulence issues, unlike chickpeas. However, overindulgence can lead to gastritis and stomach pain. Allergic reactions to these beans are rare. For more information, please refer to medical disclaimer.
You may also like to read ≻≻
Adzuki beans nutrition facts and health benefits.
Chickpeas nutrition facts and health benefits.
Lima beans nutrition facts and health benefits.
Fava beans nutrition facts and health benefits.
Soybeans nutrition facts and health benefits.
≻≻- Back to Legumes from Black Gram. Visit here for an impressive list of vegetables with complete illustrations of their nutrition facts and health benefits.
≻≻- Back to Home page.
Further Resources:
Stanford School of Medicine Cancer information Page- Nutrition to Reduce Cancer Risk.