Spearmint Nutrition facts
Spearmint herb (garden mint or common mint) has long been reputed for its characteristic aroma it imparts to the recipes. The least pungent and subtle among the species of the mint family, this unique herb is one of the chef’s favorite culinary ingredients all over the world.
Garden Mint herb botanically belongs to the family of Lamiaceae, in the Genus: Mentha. Scientific name: Mentha spicata.

|

|
| Spearmint herb. Note for oval, deep green leaves with serrated margins. Photo courtesy: sandy austin |
Mentha spicata-potherb. Photo: notahipster |
Spearmint is a branching perennial herb of Mediterranean origin. It is widely used across Europe and in large parts of Asia and Africa in flavored drinks, salads, confectionaries, and as a garnish to recipes.
The herb grows easily in fertile, moist, and loose soil conditions. It spreads through a wide network of underground runners. Generally, small stems (divisions) are planted to propagate. It reaches about 75 cm in height and bears oppositely arranged leaves all along its thick square stem. Spearmint leaves are deep green, deeply-veined, oval in shape with pointed ends and serrated margins. Slim pointed spikes of mauve flowers appear during late summer.
There are at least 20 species of spearmint, and their hybrids exist. However, it is difficult to classify them because of their variability and readiness to hybridize with each other. Here are some mint herbs apart from the popular peppermint and watermint;
Pineapple mint (M.suaveolens),
Ginger mint (M. x gentilis),
Japanese mint M. arvensis var.piperascens),
Corn mint (M. arvensis),
Bergamot or horsemint (M. Piperita var.citrata).
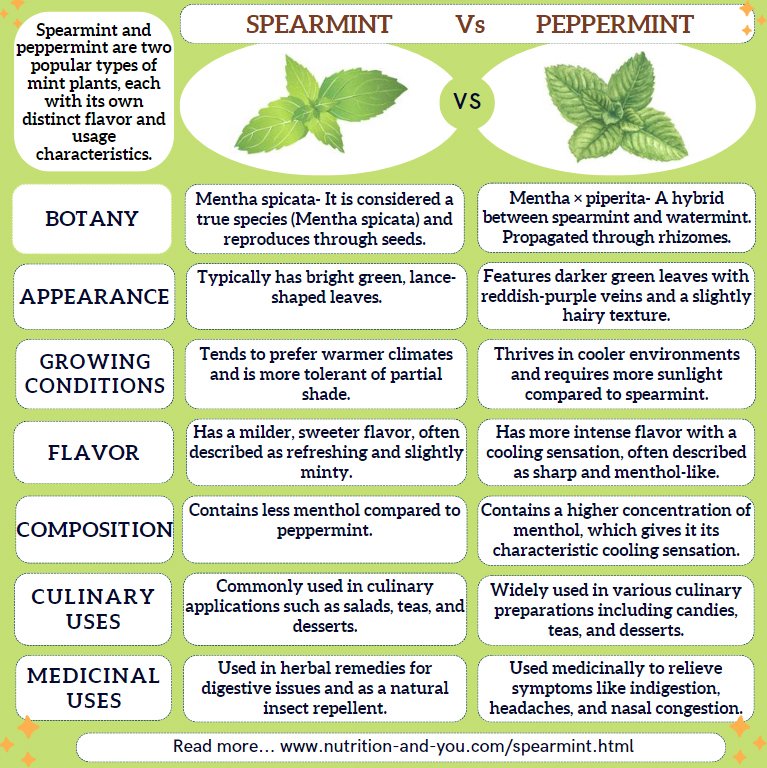
See the differences between spearmint and peppermint plants depicted in an infographic.:
 |
Health benefits of Spearmint
Spearmint is a pleasantly aromatic herb, packed with numerous health-benefiting vitamins, antioxidants, and phytonutrients.
Its leaves and herb parts carry essential oil, menthol. Unlike peppermint, spearmint leaves compose only small amounts of menthol, 0.5% compared to 40% in peppermint. Less menthol content would make this herb the least pungent and subtly fragrant herb in the mint family.
The herb has low calories (about 43 calories per 100 g) and contains zero cholesterol.
The chief essential oil in spearmint is menthol. Other important chemical components of spearmint are alpha-pinene, ß-pinene, carvone, cineole, linalool, limonene, myrcene and caryophyllene. These compounds in mint help relieve fatigue and stress.
The herb parts are also very good in minerals like potassium, calcium, manganese, iron (148% of RDA), and magnesium. Iron is essential for enzymes in cellular metabolism and the synthesis of hemoglobin. Potassium is an important component of cells and body fluids that helps control heart rate and blood pressure. The human body utilizes manganese as a co-factor for the antioxidant enzyme, superoxide dismutase.
Further, the herb is also rich in many antioxidant vitamins, including vitamin-A (provides 4054 IU or 135% of RDA), β-carotene, vitamin-C, folates (26% of RDA), vitamin B-6 (pyridoxine), riboflavin and thiamin.
Medicinal uses of Spearmint
Almost all parts of spear mint herb found a place in various traditional as well in modern medicine.
The herb decoction is an excellent remedy for minor ailments such as headaches, nervous strain, fatigue, and stress, as well as for respiratory problems; helps to relieve asthma, bronchitis, and catarrh.
It is very useful for dealing with digestive problems, including nausea, flatulence, and hiccups as it relaxes the stomach muscles.
The essential oil, menthol, has analgesic, local anesthetic, and counterirritant properties. Menthol also found application in the preparation of toothpaste and mouth fresheners.
On the skin, when used as cream or lotion, it may help relieve itching, dermatitis, and hives.
Spearmint oil is used as a blended massage oil and in aromatic therapy to help relieve headaches, stress, fatigue, and nervous conditions and to relieve itching.
When taken within limits, spearmint tea can be used safely in pregnancy. In women, it helps reduce unwanted hairs through its anti-androgenic properties.(Medical disclaimer)
| See the table below for in-depth analysis of nutrients: Spearmint (Mentha spicata), fresh, Nutritional value per 100 g. (Source: USDA National Nutrient data base). |
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percent of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 44 Kcal | 2% |
| Carbohydrates | 8.41 g | 6.5% |
| Protein | 3.29 g | 6% |
| Total Fat | 0.73 g | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 6.8 g | 18% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 105 µg | 26% |
| Niacin | 0.948 mg | 6% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.158 mg | 12% |
| Riboflavin | 0.175 mg | 13.5% |
| Thiamin | 0.078 mg | 6.5% |
| Vitamin A | 4054 IU | 135% |
| Vitamin C | 13.3 mg | 22% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 30 mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 458 mg | 64% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 199 mg | 20% |
| Copper | 0.240 mg | 75% |
| Iron | 11.87 mg | 148% |
| Magnesium | 63 mg | 16% |
| Manganese | 1.118 mg | 48.5% |
| Zinc | 1.09 mg | 10% |
Selection and storage
Fresh spearmint leaves can be available all around the year. The herb is grown in much similar fashion to that of peppermint, basil, oregano, etc. It can be grown in pots, as a garden herb, or cultivated on a larger scale as a field crop for the purpose of extraction of essential oils. In general, its leaves are harvested just before the flowering stage for culinary purposes. However, the whole plant may be gathered in full flower for the distillation of essential oils.
In the herb store, spearmint leaves and stems, fresh or dried, can be made available. Choose spearmint leaves that are fresh, and bright green, imparting a spearmint scent. Avoid wilted, yellow, and floral leaves.
Once at home, wash the leaves in clean running water, pat dry with absorbent paper, and store in the vegetable compartment of the refrigerator for use in the near future.

|
| Dried spearmint herb. |
Dried spearmint is also preferred in cooking, especially in the preparation of teas/drinks. To dry, spread its leaves on a plastic sheet and allow to dry under shade. Thus dried herb parts should be stored in an airtight container, stored in a cool place away from sunlight.
Preparation and serving methods
Unlike in other mint species, spearmint contains very minimal quantities of menthol, hence less harsh and pungent, making it one of the most preferred herbs in cooking, confectionery, and health drinks.
Here are some serving tips:
 |
| Brewing Spearmint herb tea. Photo: storebukkebruse |
Its fresh leaves, either chopped or ground, can be added to the salads.
It is good for making mint sauce. To prepare mint sauce, ground fresh mint leaves mixed with yogurt, cumin, and a little salt.
The herb is also used as a flavoring agent in ice creams, jams, cakes, jelly, etc.
Spearmint tea is a popular drink.
The herb is also used in cooking recipes. In general, it is added in small amounts, chopped or ground, to recipes at the final stages of cooking in order to retain its flavor and taste.
Safety profile
Handling mint herbs may cause skin rashes and irritation in some sensitized individuals and should be handled with care, using protective gloves. (Medical disclaimer).
≺≺ Back to Herbs from Spearmint. Visit here for an impressive list of all varieties of herbs with complete illustrations of their nutrition facts and health benefits.
≺≺ Back to Home page.
Further Resources:
USDA National Nutrient Database. (opens in new window).
Stanford School of Medicine Cancer information Page-Nutrition to Reduce Cancer Risk (Link opens in new window).